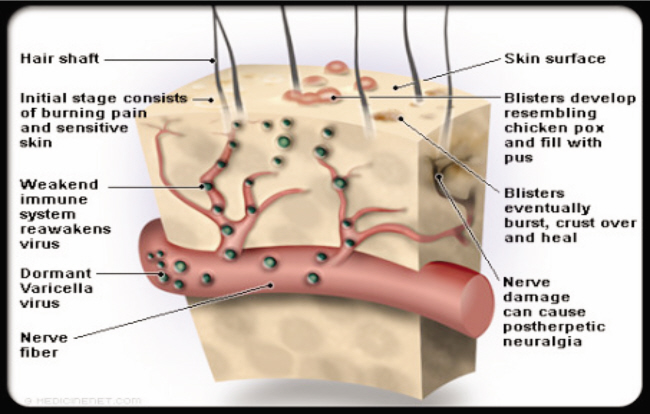
 Shingles also known as Herpes Zoster causes a painful rash that usually is located on one side of the body. Shingles is caused by the varicellazoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus can enter the nervous system and lie dormant for years. Eventually it may reactivate and travel along nerve pathways to the skin causing shingles. Shingles tends to occur in seniors, especially during periods of low immunity or high stress.
Shingles also known as Herpes Zoster causes a painful rash that usually is located on one side of the body. Shingles is caused by the varicellazoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus can enter the nervous system and lie dormant for years. Eventually it may reactivate and travel along nerve pathways to the skin causing shingles. Shingles tends to occur in seniors, especially during periods of low immunity or high stress.
Is it Contagious?
A person with shingles can pass the varicellazoster virus to anyone who isn’t immune to chickenpox. This usually occurs through direct contact with the open sores of the shingles rash. Once infected, the person will develop chickenpox, not shingles. Chickenpox can be dangerous for some groups of people such as pregnant women, newborn babies, and persons with weak immune systems.
What are the signs and symptoms of shingles?
- Pain, burning, tingling and numbness
- Fluid-filled tiny blisters that break open and crust
- Itching
- Headache, fatigue, fever are less common
What are the potential complications?
- Post-herpetic neuralgia or pain that continues long after the blisters have cleared
- Vision loss in or around the eyes
- Inflammation of the brain (encephalitis), facial paralysis, hearing or balance problems
- Skin infections
What treatment options are available?
Antiviral drugs such as Valcylovir (Valtrex), Famciclovir (Famvir) or Acyclovir (Zovirax) can speed up healing and reduce complications. To reduce the pain, anticonvulsants such as gabapentin or tricyclic antidepressants may be prescribed. Numbing agents such a lidocaine skin patch also reduce the pain.
How can a person prevent shingles?
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the use of the varicella-zoster vaccine (Zostavax) for adults age 50 and older. It is a one-time vaccination. In scientific studies, the vaccine reduces the risk of developing shingles by about 50 percent. It will reduce the course and severity of the disease as well as reduce the risk of post-herpetic neuralgia. Since the vaccine contains live virus it should not be given to people who have weakened immune systems.


Leave a Reply