Signs of Stroke
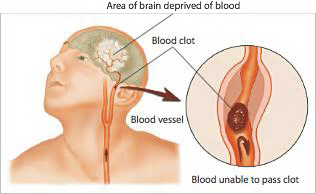 Each year in the United States, there are more than 700,000 strokes. Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the country. A stroke is a medical emergency. It occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is reduced or interrupted. Nearly three-quarters of all strokes occur in people over the age of 65. It is the leading cause of long-term disabilities. African Americans have a higher death rate from stroke compared to any other ethnic group in the US.
Each year in the United States, there are more than 700,000 strokes. Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the country. A stroke is a medical emergency. It occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is reduced or interrupted. Nearly three-quarters of all strokes occur in people over the age of 65. It is the leading cause of long-term disabilities. African Americans have a higher death rate from stroke compared to any other ethnic group in the US.
Warning Signs of Stroke
- Sudden weakness or numbness of face, arm, or leg
- Sudden confusion, difficulty understanding or speaking
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Sudden difficulty walking, balance loss, or coordination
- Act fast, call 9-1-1
What is a mini stroke?
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) is known as a mini stroke in which the signs and symptoms of stroke resolve within 24 hours. It happens when the blood flow to a part of the brain is temporarily reduced often by a blood clot, after a short time the blood flows again and the symptoms go away. A mini stroke is a warning sign, it means that a person is likely to have a stroke in the future.
How is stroke diagnosed?
The first test after a stroke is typically a CT scan of the brain. This test will help the doctor diagnose whether the stroke is ischemic (caused by a blot clot) or hemorrhagic (caused by a bleed). MRI may also be done to find out the amount of damage to the brain and help predict recovery. CT or MRI angiograms take a closer look at the circulation in the brain.
How is stroke treated?
Thrombolytic (clot-buster) drugs help reestablish blood flow to the brain by dissolving the clots, which are blocking the flow. To be effective, should be given as quickly as possible in the recommended 4.5 hour window. Aspirin or antiplatelet medication may be prescribed. Treatment of blood pressure, cholesterol and diabetes is important.
What is stroke rehabilitation?
Most persons are disabled following a stroke. The types and degrees of disability that follow a stroke depend upon which area of the brain is damaged and how much is damaged. Recovery depends on rehabilitation with physical, occupational, and speech therapy. Rehabilitation helps stroke survivors relearn skills that are lost when part of the brain is damaged.
Is stroke preventable?
Studies show that 80% of stroke is preventable. It is important to control personal risk factors. Good control of blood pressure, cholesterol and diabetes reduce the likelihood of getting a stroke. Eating right and exercise will also reduce a person’s risk. Eat five servings of fruits and vegetables daily. Quit smoking and drink alcohol in moderation.


Leave a Reply