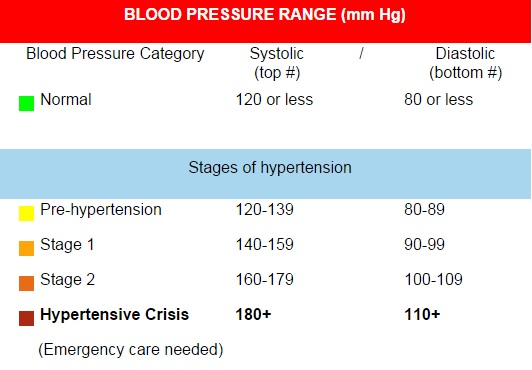
 One in three adults in the U.S. has high blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of the blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps blood. If pressure stays high over time it will damage the body. Hypertension is the persistent elevation of blood pressure. Blood pressure rises with age and is a common health problem in seniors. The only way to tell whether you have high blood pressure is to have your blood pressure measured with a blood pressure cuff (sphygmomanometer). This is usually done in a doctor’s office. It is important to know your blood pressure numbers. “Systolic” (the top number) refers to blood pressure when the heart beats while pumping blood. “Diastolic” (the bottom number) refers to blood pressure when the heart is at rest between beats.
One in three adults in the U.S. has high blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of the blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps blood. If pressure stays high over time it will damage the body. Hypertension is the persistent elevation of blood pressure. Blood pressure rises with age and is a common health problem in seniors. The only way to tell whether you have high blood pressure is to have your blood pressure measured with a blood pressure cuff (sphygmomanometer). This is usually done in a doctor’s office. It is important to know your blood pressure numbers. “Systolic” (the top number) refers to blood pressure when the heart beats while pumping blood. “Diastolic” (the bottom number) refers to blood pressure when the heart is at rest between beats.
What are the symptoms of high blood pressure?
Most people do not have any symptoms. Rarely headaches may occur. Often seniors find out too late that they have high blood pressure after damage has occurred to the heart, brain or kidneys.
What are the complications of untreated high blood pressure?
High blood pressure is a silent killer. It causes stroke, heart attack, heart failure, kidney failure and may even lead to blindness. High blood pressure and its complications are a common cause of disability in seniors.
What are the causes of high blood pressure?
- Genetics
- Family history of high blood pressure
- Older age
- Lifestyle factors, such as obesity, lack of physical activity, increased alcohol use, high salt diet, smoking
Illicit drugs, such as cocaine or ice
- Medications, such as steroids, hormone replacement therapy
- Chronic kidney disease
- Thyroid and adrenal gland disorders
- Sleep apnea
What are the treatment approaches to high blood pressure?
- Healthy lifestyle: exercise, avoid smoking, limit alcohol, weight reduction
- Manage everyday stress
- Blood pressure lowering medications are often needed for life, and once blood pressure is under control it is important to continue to take the prescribed medications
- Aspirin to be taken daily to prevent heart attack and stroke
What is the DASH diet?
Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) is a flexible and balanced eating plan.
 Low in saturated fat, cholesterol and total fat
Low in saturated fat, cholesterol and total fat
- Low in salt
- Focuses on fruits, vegetables and fat-
free or low- fat dairy products
- Rich in whole grains, fish, poultry, beans, seeds and nuts
- Contains fewer sweets, added sugars and sugary beverages and red meats than the typical American diet


Leave a Reply